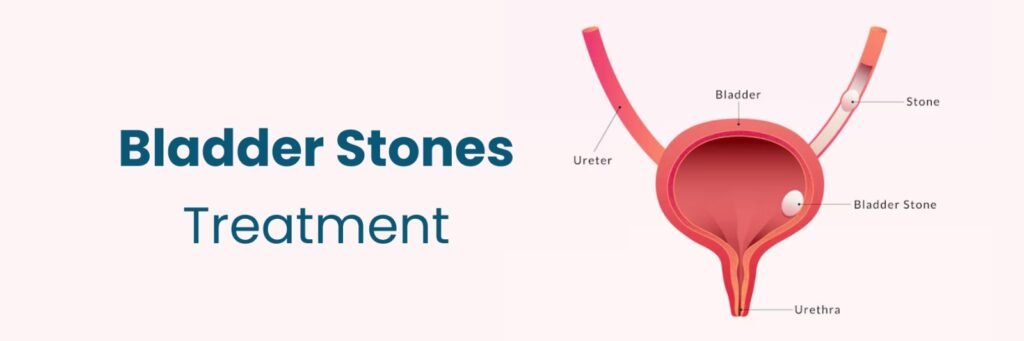
Bladder and ureteric stones are hard mineral deposits that form in the urinary system. They can cause pain, discomfort, and urinary problems if left untreated. Understanding their causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for maintaining urinary health.
At Vardan Hospital, we offer:
Specialized laser lithotripsy techniques for faster recovery.
Tailored treatment plans to suit each patient's condition.
Faster healing, reduced pain, and minimal hospital stay.
Comprehensive lifestyle and dietary advice to prevent future stone formation.

If you’re experiencing symptoms of bladder or ureteric stones, don’t wait for complications. Book a consultation with our experts today! Call +91 88504 57921 or visit www.vardaanspecialityhospital.com to schedule your appointment.
+91 88504 57921
vardaanspecialityhospital@gmail.com
Saurabh CHS, Sabnis Hospital, Dr, VB Phadake Rd, Gavanpada, Mulund East, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400081
Saurabh CHS, Ground Floor, Dr. VB Phadake Rd, Gavanpada, Mulund East, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400081