Urinary tract infections (UTIs) are infections that can occur in any part of the urinary system, including the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. Most UTIs affect the lower urinary tract – the bladder and the urethra and are more common in women than men.
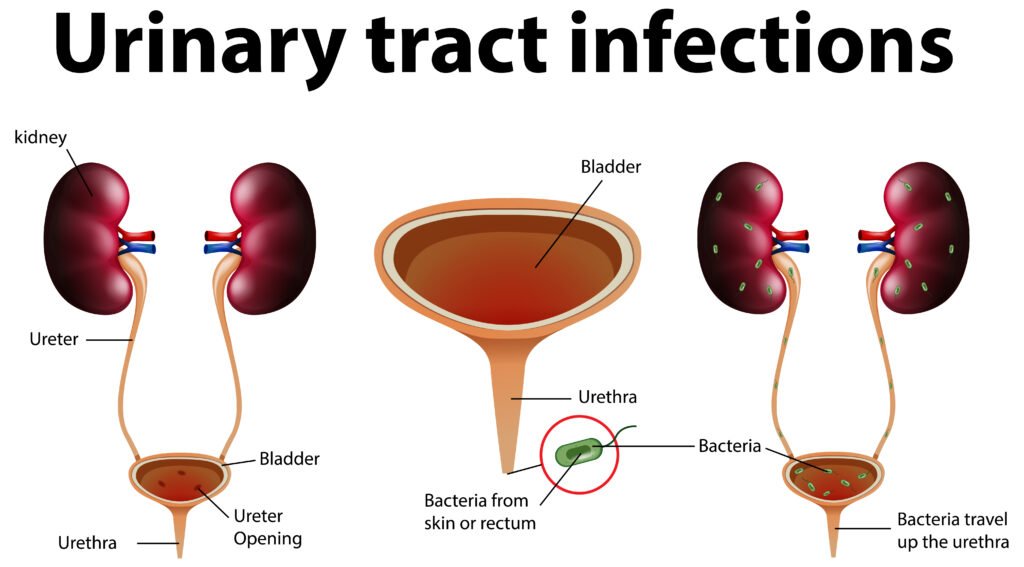
UTIs are caused by bacteria, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli), which normally live in the intestines. These bacteria can enter the urinary tract through the urethra, leading to infection. Risk factors include:
Treatment depends on the severity and location of the infection:
Mild UTIs: Usually treated with oral antibiotics and hydration. Symptoms typically improve within a few days.
Severe or recurrent UTIs: May require longer antibiotic courses or intravenous antibiotics if the infection has spread to the kidneys.
Pain relief: Medications can be provided to ease discomfort during urination.
Drink plenty of water to flush bacteria from the urinary tract.
Urinate frequently and avoid holding urine for long periods.
Wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacterial spread.
Urinate after sexual activity to help flush bacteria from the urethra.
Avoid irritating products, like harsh soaps or feminine sprays, near the genital area.
If you experience symptoms like burning urination, pelvic pain, or fever, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider promptly to prevent complications such as kidney infections.
At Vardan Hospital,, we understand how disruptive and uncomfortable UTIs can be. Our dedicated urology team offers comprehensive diagnostic services and personalized treatment plans to help you recover quickly and reduce the risk of recurrence.
Our urologists specialize in diagnosing and treating all types of UTIs, from simple infections to recurrent and complicated cases.
We use state-of-the-art lab tests and imaging techniques to identify the exact cause of your infection.
We tailor your treatment plan based on your medical history and individual needs.
We provide education and lifestyle recommendations to help prevent future infections.

If you’re experiencing symptoms of a UTI or have recurrent infections, don’t wait. Schedule a consultation with our experienced urology team today.
+91 88504 57921
vardaanspecialityhospital@gmail.com
Saurabh CHS, Sabnis Hospital, Dr, VB Phadake Rd, Gavanpada, Mulund East, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400081
Saurabh CHS, Ground Floor, Dr. VB Phadake Rd, Gavanpada, Mulund East, Mumbai, Maharashtra 400081